Home insurance is a type of insurance policy that protects your house and belongings against various risks like fire, theft, natural disasters, and accidental damage. It usually covers:
- The structure of your home (walls, roof, etc.)
- Your personal belongings inside the home (furniture, electronics, clothes)
- Liability protection if someone is injured on your property
The purpose of home insurance is to provide financial support so you can repair or replace your property and belongings if they’re damaged or lost due to covered events.
Key Takeaway
- Home insurance protects your property and belongings against various risks such as fire, theft, natural disasters, and accidental damage, providing financial security.
- Coverage typically includes the structure of your home, your personal belongings, and liability protection in case someone is injured on your property.
- Not all risks are covered automatically; common exclusions include wear and tear, pest damage, and certain natural disasters like floods and earthquakes unless you add specific riders.
- Choosing the right policy requires assessing your home’s value, understanding inclusions and exclusions, and considering your location’s risk factors.
- Premiums are influenced by factors like the property’s value, location, coverage amount, and any additional riders or add-ons you choose.
- Reviewing the insurer’s claim settlement ratio and customer service reputation is crucial to ensure smooth and reliable claim processing.
- Regularly review and update your home insurance policy to ensure it continues to meet your needs as your home or possessions change over time.
- Additional riders or separate policies may be needed for full protection against risks such as floods or earthquakes, depending on your area.
Understanding Home Insurance

Home insurance is a type of insurance policy designed to protect homeowners from financial losses related to their home and personal property. It acts as a safety net against unexpected events that could cause damage or loss, such as fire, theft, natural disasters, or accidents.
What Does Home Insurance Cover?
Home insurance typically provides coverage in three main areas:
Structure Coverage (Building Insurance):
This protects the physical structure of your home, including the walls, roof, floors, built-in appliances, and any permanent fixtures like cabinets or plumbing. If your house is damaged by a covered peril—like fire, storm, or vandalism—this part of your policy helps cover repair or rebuilding costs.
Contents Coverage (Personal Property Insurance):
This covers your personal belongings inside the home, such as furniture, electronics, clothing, jewelry, and appliances. If these items are stolen or damaged by covered risks, home insurance can reimburse you for their value.
Liability Protection:
This covers you in case someone gets injured on your property and decides to sue you. It can help cover legal fees and medical expenses, protecting you from significant financial loss.
Types of Risks Covered
Home insurance is designed to protect you against a variety of risks that could cause damage to your property or belongings. However, the exact risks covered can vary depending on the insurance policy and provider. Understanding these risks helps you choose the right plan and know what to expect in case of a claim.
Common Risks Typically Covered
Fire and Smoke Damage
One of the most fundamental protections, home insurance covers damage caused by fire and smoke. This includes accidental fires originating inside the home or fires from external sources that spread to your property.
Theft and Burglary
If your home is broken into and your possessions are stolen or vandalized, your home insurance policy usually covers the loss. This applies to stolen items as well as any damage caused by forced entry.
Vandalism and Malicious Damage
Deliberate damage caused by vandals, such as broken windows, graffiti, or property destruction, is generally covered under home insurance.
Natural Disasters and Weather Events
Many policies cover damage caused by certain natural disasters like:
- Storms and hailstorms
- Lightning strikes
- Tornadoes or cyclones
- Floods (often require separate flood insurance or rider)
- Earthquakes (may need additional earthquake coverage)
It’s important to verify which natural disasters are included in your policy because coverage can vary greatly depending on location and insurer.
Water Damage
Water damage resulting from burst pipes, leaks, or accidental overflow is often covered. However, damage caused by gradual seepage or poor maintenance might not be.
Explosion
Damage caused by explosions, whether due to gas leaks or other reasons, is usually covered by home insurance.
Falling Objects
If trees, branches, or other objects fall on your home causing damage, your policy may cover the repairs.
Liability Risks
Home insurance also provides liability protection. If someone gets injured on your property, and you’re found legally responsible, your policy can cover medical expenses and legal fees.
Risks Typically Excluded or Limited
While home insurance covers many risks, there are certain exclusions or limitations to be aware of:
- Wear and Tear: Damage due to aging, deterioration, or lack of maintenance is not covered.
- Pest Infestations: Damage from termites, rodents, or insects is generally excluded.
- Floods and Earthquakes: Often excluded unless specifically added through riders or separate policies.
- Intentional Damage: Damages caused intentionally by the homeowner or residents are not covered.
- Nuclear Hazards: Damage caused by nuclear events is typically excluded.
- Mold and Fungus: Damage due to mold growth may be excluded unless caused by a covered peril.
Why Knowing the Covered Risks Matters
Understanding what risks your home insurance plan covers helps you:
- Choose the right level of protection based on your home’s location and vulnerabilities.
- Decide whether you need additional riders or policies for specific risks like floods or earthquakes.
- Avoid surprises when filing a claim by knowing what is excluded.
Final Thought
When shopping for home insurance, always read the policy documents carefully to understand the list of covered perils and exclusions. Some insurers offer “all-risk” or “comprehensive” policies that cover a wider range of risks, while others may have more limited protection.
Why Is Home Insurance Important?

Owning a home is often the largest financial investment most people make in their lifetime. Protecting that investment is critical, and home insurance provides that essential protection. Here’s why home insurance matters:
Protects Your Financial Investment
Your home represents a significant portion of your net worth. If unforeseen events like fire, theft, natural disasters, or accidents damage your property, the cost of repairs or rebuilding can be enormous. Home insurance helps cover these expenses, so you don’t have to bear the full financial burden alone.
Covers Loss or Damage to Personal Belongings
Home insurance isn’t just about the structure—it also protects your personal belongings inside the home. Furniture, electronics, clothing, jewelry, and other valuables can be expensive to replace. Insurance helps reimburse you for lost or damaged items due to covered risks.
Provides Liability Protection
Accidents can happen anywhere, including your home. If a visitor is injured on your property and decides to sue for damages, home insurance can cover legal fees, medical expenses, and settlements. This liability protection shields you from potentially devastating financial claims.
Offers Peace of Mind
Having home insurance means you can rest easier knowing you’re financially protected against many risks. It reduces the stress and uncertainty of facing expensive repairs or replacements after a loss.
Often Required by Mortgage Lenders
Most mortgage lenders require borrowers to have home insurance as a condition for the loan. This protects the lender’s interest in the property, ensuring the home can be repaired or rebuilt if damaged.
Helps with Temporary Living Expenses
If your home becomes uninhabitable due to a covered event, many home insurance policies provide coverage for additional living expenses, like hotel stays or temporary rentals, while your home is being repaired.
Encourages Risk Management and Safety
Having home insurance often encourages homeowners to adopt safety measures such as installing smoke detectors, security systems, and fire extinguishers. These not only reduce risk but may also qualify you for premium discounts.
Summary
Home insurance is vital because it protects your biggest asset, covers your belongings, offers liability protection, and provides peace of mind. It helps you recover financially from unexpected events that could otherwise cause severe hardship. Whether or not required by a lender, having home insurance is a smart, responsible choice for any homeowner.
How Does Home Insurance Work?
When you buy home insurance, you agree to pay a premium—usually monthly or yearly—to the insurance company. In exchange, the insurer agrees to cover costs related to specified risks outlined in the policy.
If a covered loss happens, you file a claim with the insurer. The insurer then evaluates the claim and, if approved, pays out funds to repair damages or replace lost items up to the coverage limits.
Key Terms to Know
Understanding the basic terminology can make it easier to choose and manage your home insurance policy. Here are some of the most important terms:
Premium
The amount you pay to the insurance company, usually monthly or annually, to keep your home insurance policy active.
Deductible
The portion of a covered loss you pay out-of-pocket before the insurance company pays the rest. For example, if your deductible is $1,000 and you have a claim for $5,000, you pay $1,000 and the insurer pays $4,000.
Coverage Limit (Sum Insured)
The maximum amount an insurer will pay for a covered loss. It’s important that this amount reflects the true value of your home and belongings.
Claim
A formal request you submit to your insurance company for payment after experiencing damage or loss covered by your policy.
Exclusions
Specific situations, events, or items that are not covered by your insurance policy. For example, many home insurance plans exclude damage caused by floods or earthquakes unless you purchase additional coverage.
Liability Coverage
Protection against legal responsibility if someone is injured on your property or if you accidentally cause damage to someone else’s property.
Replacement Cost
The amount needed to replace or repair damaged property without deducting for depreciation.
Actual Cash Value (ACV)
The replacement cost minus depreciation. It represents the current market value of the item or property.
Rider (Add-On)
Additional coverage options that you can purchase to extend or enhance your standard home insurance policy, such as coverage for valuable jewelry, floods, or earthquakes.
Waiting Period
The time frame between purchasing the policy and when coverage begins or before certain benefits take effect.
Underwriting
The process insurance companies use to evaluate risk and decide whether to accept an application and at what premium.
Summary
Familiarizing yourself with these key terms helps you better understand your home insurance policy, make informed decisions, and communicate effectively with your insurer. If you’d like, I can help explain any specific terms further or assist in comparing policies!
Factors to Consider When Choosing a Home Insurance Plan
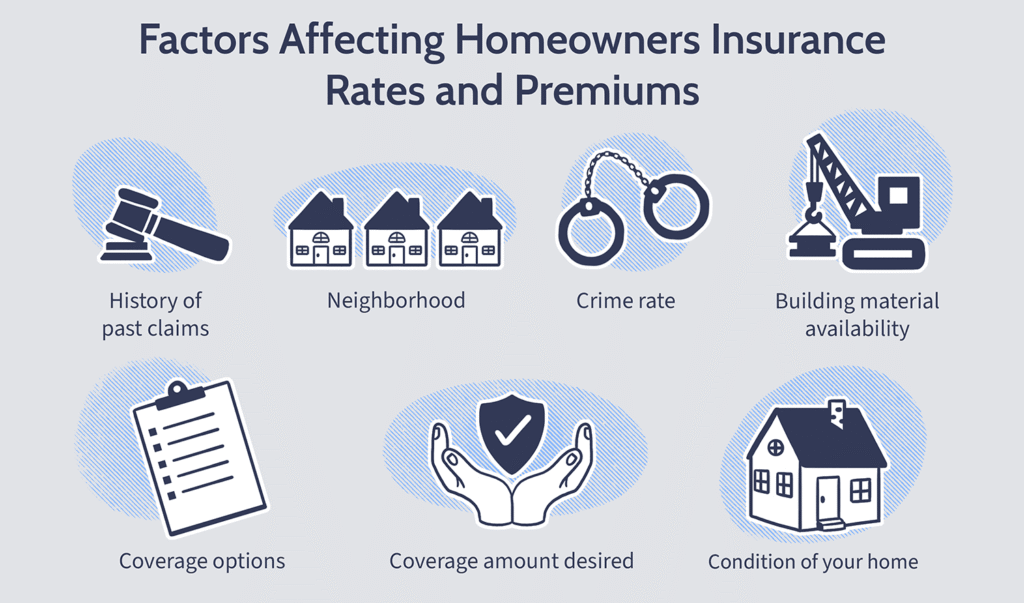
Selecting the right home insurance plan is crucial to ensure your property and belongings are adequately protected. Since every homeowner’s needs differ, it’s important to carefully evaluate several factors before purchasing a policy. Here’s what you should consider:
Assess Your Coverage Needs
Start by evaluating the value of your home and personal possessions. Calculate the cost to rebuild your house in case of a total loss and estimate the worth of your belongings. This helps determine the right coverage amount or sum insured. Undervaluing your property can lead to inadequate compensation during a claim.
Understand Policy Inclusions and Exclusions
Every insurance policy outlines specific risks it covers (inclusions) and those it doesn’t (exclusions). It’s essential to read the policy document carefully to avoid surprises later. For example, some policies may exclude damage caused by floods or earthquakes unless you opt for additional coverage.
Evaluate the Claim Settlement Ratio (CSR)
The Claim Settlement Ratio indicates how many claims an insurer successfully settles compared to the total claims filed. A higher CSR reflects reliability and promptness in claim payouts. Choose an insurer with a strong CSR to ensure your claims are handled efficiently.
Choose the Right Policy Type
Home insurance policies vary mainly between:
- Market Value Policy: Pays the current market value of damaged property, factoring in depreciation.
- Reinstatement Value Policy: Covers the actual cost to repair or rebuild the home without accounting for depreciation.
A reinstatement value policy generally offers better protection, especially for new homes or properties with high replacement costs.
Consider Additional Riders and Add-Ons
Many insurers offer riders that extend coverage beyond standard protection. These might include:
- Coverage for home appliances and electronics
- Personal accident coverage
- Loss of rent protection if your home becomes uninhabitable
- Coverage for jewelry or valuable collections
Assess which add-ons match your lifestyle and needs.
Review Premium Costs and Payment Terms
Compare premium amounts among different insurers, keeping in mind that the cheapest option isn’t always the best. A low premium might mean limited coverage. Also, understand the payment schedule—whether premiums are paid monthly, quarterly, or annually—and any penalties for late payments.
Check the Insurer’s Reputation and Customer Service
Research the insurance provider’s reputation, financial strength, and customer service. Read customer reviews and testimonials to gauge satisfaction levels. Responsive customer support can make a significant difference, especially during the claims process.
Understand the Deductible Amount
The deductible is the amount you pay out-of-pocket before the insurance coverage kicks in. Policies with higher deductibles often have lower premiums, but you need to be comfortable with the deductible amount in case of a claim.
Location and Risk Factors
Your home’s location affects your insurance needs and premium rates. Properties in flood-prone or earthquake-prone areas may require special coverage, often at higher costs. Understanding these risks helps tailor your policy accordingly.n, customer service quality, and claim settlement process. Reading customer reviews and ratings can provide insights into the insurer’s reliability and responsiveness.
Also Read: Which Home Insurance Plan Is Right for You?
Conclusion
Selecting the right home insurance plan involves a thorough assessment of your property’s value, understanding the policy’s inclusions and exclusions, and evaluating the insurer’s reputation and claim settlement process. By considering these factors, you can ensure that your home and belongings are adequately protected, providing you with peace of mind and financial security.
FAQs
Q1: Is home insurance mandatory in India?
While home insurance is not legally mandatory in India, it is highly recommended to protect your property and belongings from unforeseen events.
Q2: Can I insure only the contents of my home?
Yes, many insurers offer contents-only policies, allowing you to insure only your personal belongings.
Q3: Does home insurance cover natural disasters?
Home insurance policies in India typically cover natural disasters like fire, earthquakes, and floods. However, it’s essential to verify the specific inclusions in your policy.
Q4: How is the premium for home insurance calculated?
The premium is calculated based on factors like the property’s value, location, construction type, and the chosen coverage.
Q5: Can I transfer my home insurance policy if I sell my property?
Home insurance policies are generally non-transferable. It’s advisable to cancel the existing policy and purchase a new one for the new property.
Q6: What is the waiting period for a home insurance claim?
The waiting period varies by insurer and policy type. It’s crucial to understand the waiting period before purchasing the policy.
Q7: Are there any discounts available on home insurance premiums?
Some insurers offer discounts for installing safety devices like smoke detectors or burglar alarms. Additionally, bundling home insurance with other policies may also lead to discounts.



